The Potential Impact of the USD Rally on Global Economics
Fundamentals behind the US Dollar’s Potential Rally
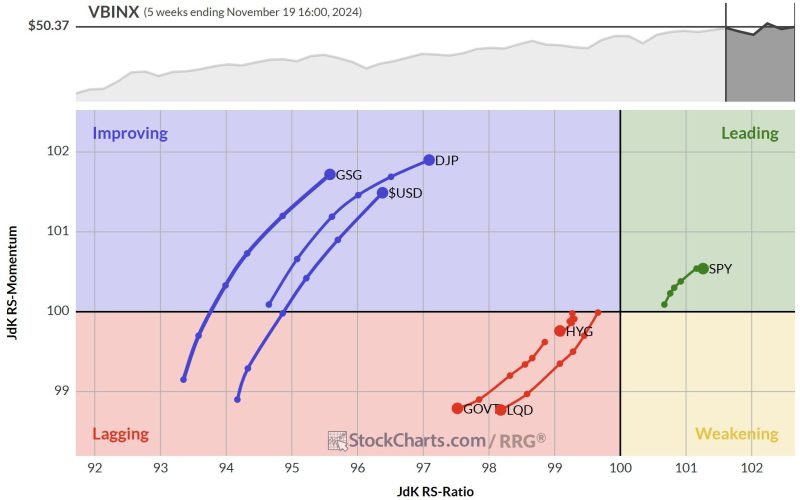
The US dollar, as a global reserve currency, plays a vital role in the international financial markets. A potential rally in the USD could have significant implications for various sectors globally. Several fundamental factors are driving the potential rally of the USD, including the Federal Reserve’s policy divergence from other central banks, robust economic growth, higher interest rates, and geopolitical uncertainties. These factors collectively create a favorable environment for the USD to strengthen against other major currencies.
Policy Divergence and Interest Rate Hikes
One of the key factors contributing to the potential USD rally is the divergence in monetary policy between the Federal Reserve and other central banks. The Federal Reserve has been more aggressive in raising interest rates compared to other central banks, creating a higher yield on US assets. This attracts foreign investors looking for higher returns, leading to increased demand for the USD. As the interest rate differentials widen further, investors are likely to favor USD-denominated assets, further boosting the currency’s value.
Robust Economic Growth and Safe-Haven Demand
The US economy has shown resilience and robust growth compared to other major economies. The strong economic performance, supported by tax cuts, deregulation, and increased consumer spending, enhances the attractiveness of US assets for investors. In times of global economic uncertainty, investors tend to seek safe-haven assets, and the USD is often perceived as a safe-haven currency. Geopolitical tensions, trade conflicts, and economic uncertainties in other regions could drive up demand for the USD, further strengthening its value.
Impact on Global Trade and Emerging Markets
A potential USD rally could have mixed implications for global trade and emerging markets. A stronger USD makes US exports more expensive and less competitive in international markets, potentially leading to a widening trade deficit. On the other hand, it could benefit import-reliant economies by lowering their import costs. Emerging markets with high levels of USD-denominated debt could face challenges servicing their debt obligations as the USD strengthens. Central banks in these economies may need to raise interest rates to stem capital outflows and stabilize their currencies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential rally of the USD has far-reaching implications for the global economy, financial markets, and trade dynamics. The combination of policy divergence, economic strength, and safe-haven demand supports the argument for a stronger USD in the near term. While a USD rally may benefit some sectors, it could also pose challenges for others, particularly in emerging markets and trade-dependent economies. Monitoring key economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical developments will be crucial in understanding the evolving dynamics of the USD rally and its impact on the global economy.